Atherosclerosis
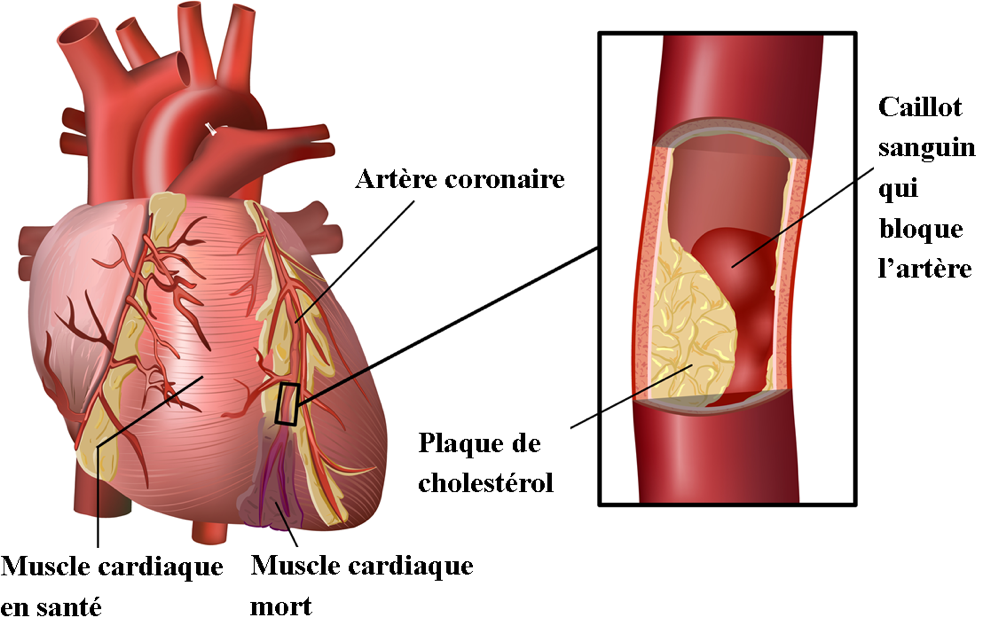
Atherosclerosis occurs when the arteries are blocked by fatty deposits (fatty tissue deposits called plaques). Atherosclerosis is a health problem that develops gradually. Although it is a normal part of aging, it can begin in childhood. Plaque can develop anywhere in the body, but it mainly affects large and medium-sized arteries, such as the coronary arteries (arteries of the heart), the arteries of the brain and the arteries of the arms and legs. Plaque contains LDL-cholesterol particles (called "bad cholesterol"), immune cells (from the inflammatory response) and various substances such as calcium. Plaque formation causes a loss of elasticity in the arteries and can lead to blockages. Blood circulation is thus slowed down or even blocked.
The majority of plaques are not "at risk"; they do not grow or grow very slowly and then stabilize. Some can reduce the opening of the coronary arteries (arteries of the heart) by up to 70%, without causing symptoms and without worsening. However, if the plaque ruptures, a blood clot can form and travel through the bloodstream, potentially blocking a smaller artery. This would then lead to an interruption of the oxygen supply to the cells, altering how they function and, in some cases, causing cell death. Therefore, interruption of the blood supply can have major consequences if it occurs in vital organs such as the heart (see diagram) and the brain, where it generates what is commonly known as a heart attack, or stroke.
Illustration of a fatty plaque in a coronary artery